Design Begins Beneath Your Feet
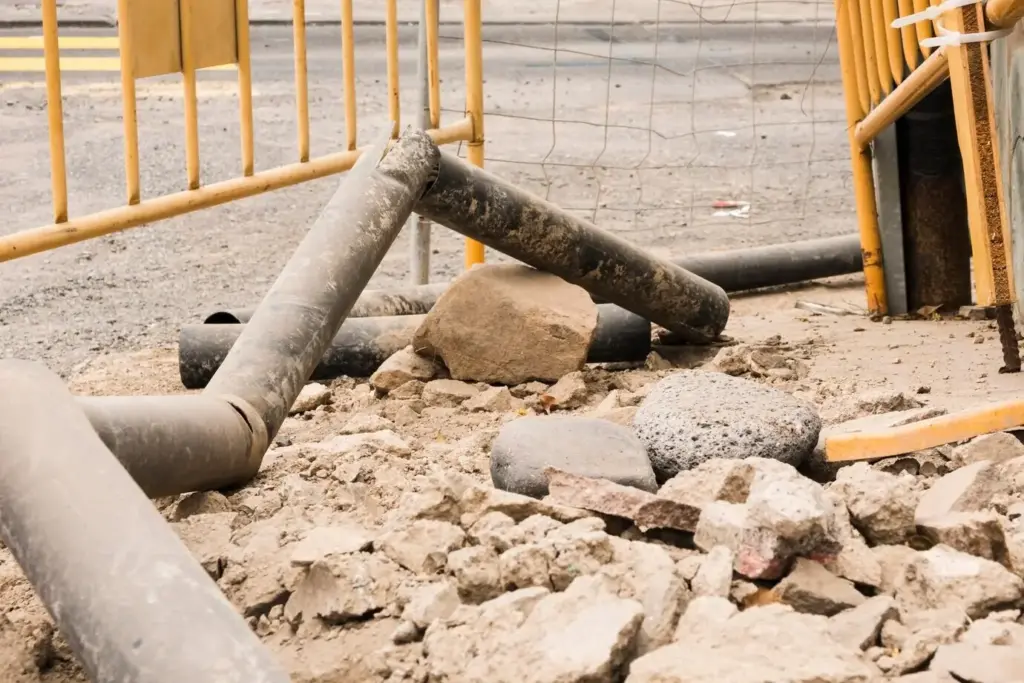

Reading the Ground Like a Designer
Texture, Structure, and the Feel Test
A handful of soil tells a long story. Ribbon it between your fingers to estimate clay, feel grittiness for sand, notice silt’s smoothness, and watch how aggregates hold together. Structure indicates pore connectivity, which governs infiltration, oxygen, and root vigor. Designers who master this tactile reading avoid generic solutions, specifying appropriate mixes and handling protocols that protect crumb structure, reduce runoff, and support predictable plant establishment across seasons and microclimates.
Chemistry, pH, and Salts That Quietly Steer Outcomes
pH nudges nutrient availability, steering which plants thrive without constant inputs. Electrical conductivity hints at salts that stress seedlings, while cation exchange capacity suggests buffering against change. A lavender bed might celebrate alkaline soil, while blueberries request acidic balance. Simple field kits guide quick decisions, yet laboratory confirmation sets durable baselines. Translate numbers into intent: fewer fertilizers, healthier roots, and planting palettes aligned with the site’s chemical temperament rather than fighting it endlessly.
Life in the Soil: Microbes, Mycorrhizae, and Invertebrates
A vibrant soil food web builds structure, cycles nutrients, moderates disease, and surprises you with resilience. Mycorrhizae extend root reach like invisible lace, while earthworms and arthropods stitch pores through dense horizons. A schoolyard garden I restored revived after a single season of compost, mulch, and reduced disturbance; respiration tests rose, and children marveled at mushrooms after the first autumn rain. Designing for life means specifying inputs and handling that keep that living engine humming.
Field Methods That Fit Creative Workflows
Site Walks, Augers, and Honest Observations
Infiltration and Percolation Without the Drama
Strength and Compaction: Penetrometers and Simple Drop Tests

Choosing the Right Panels for the Job

Interpreting Numbers Into Design Decisions

When Geotechnical Meets Horticultural
Amendments with Purpose, Not Habit

Specifications That Contractors Can Build

Commissioning and Long-Term Stewardship

All Rights Reserved.